Photo: BBC.
A PhD student found a lost city by accident in eastern Mexico, in Campeche.
Talk about happy accidents! I’m sure we have all experienced a few, whether in cooking or driving around. And we often hear of happy accidents in science. Today, we learn about an alert PHD student who found an ancient civilization without precisely looking for one.
Georgina Rannard writes at the BBC, ” ‘I was on something like page 16 of Google search and found a laser survey done by a Mexican organization for environmental monitoring,’ explains Luke Auld-Thomas, a PhD student at Tulane university in the US.
“It was a Lidar survey, a remote sensing technique which fires thousands of laser pulses from a plane and maps objects below using the time the signal takes to return.
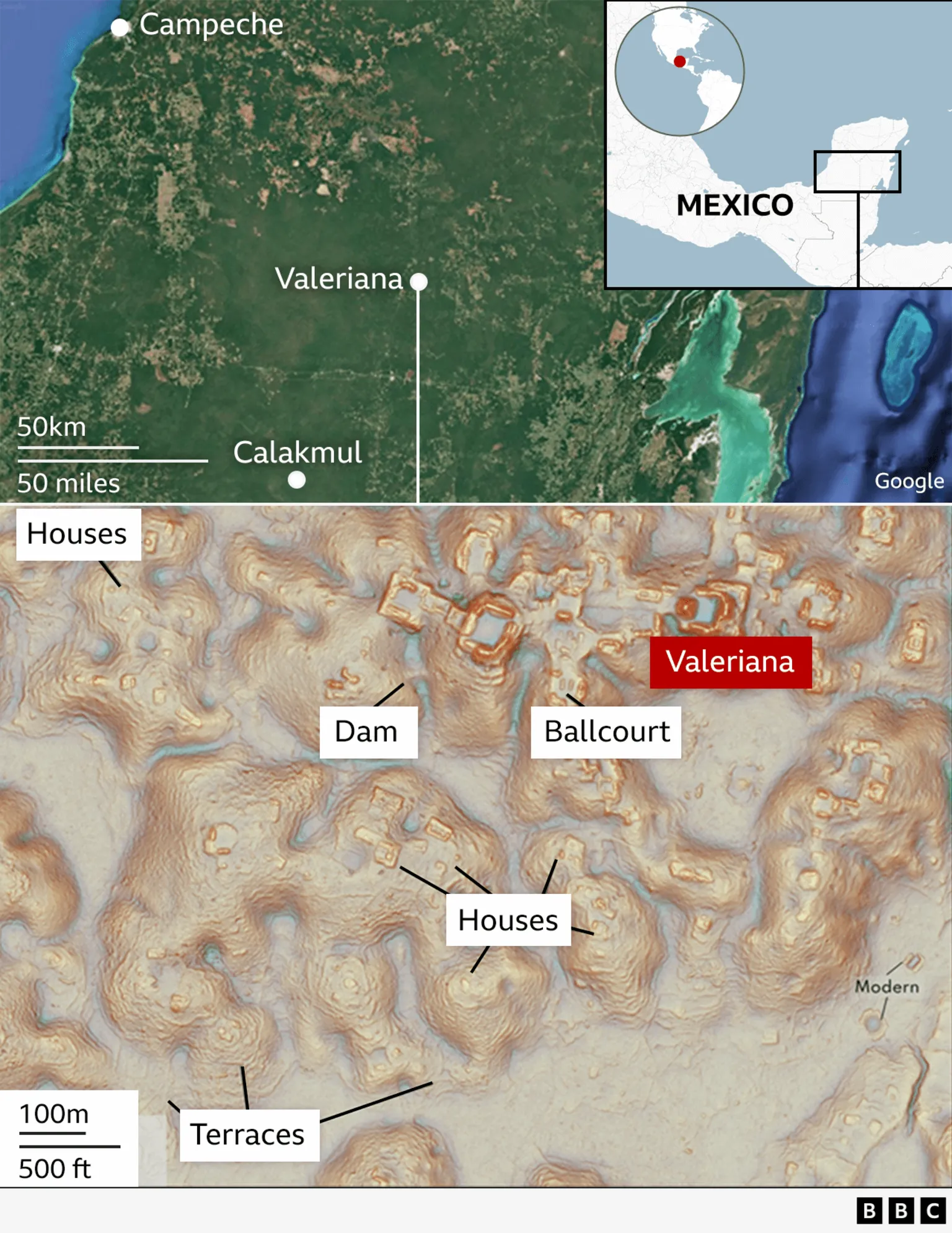
“But when Mr Auld-Thomas processed the data with methods used by archaeologists, he saw what others had missed — a huge ancient city which may have been home to 30,000-50,000 people at its peak from 750 to 850 AD. … Mr Auld-Thomas and his colleagues named the city Valeriana after a nearby lagoon.
“The find helps change an idea in Western thinking that the Tropics was where ‘civilizations went to die,’ says Professor Marcello Canuto, a co-author in the research. Instead, this part of the world was home to rich and complex cultures, he explains. …
“It is ‘hidden in plain sight,’ the archaeologists say, as it is just 15 minutes hike from a major road near Xpujil, where mostly Maya people now live.
“There are no known pictures of the lost city because ‘no one has ever been there,’ the researchers say, although local people may have suspected there were ruins under the mounds of earth.
“The city [had] two major centers with large buildings around 2km (1.2 miles) apart, linked by dense houses and causeways. It has two plazas with temple pyramids, where Maya people would have worshipped, hidden treasures like jade masks and buried their dead. It also had a court where people would have played an ancient ball game. There was also evidence of a reservoir, indicating that people used the landscape to support a large population. …
“Professor Elizabeth Graham from University College London, who was not involved in the research, says it supports claims that Maya lived in complex cities or towns, not in isolated villages. …
“The research suggests that when Maya civilizations collapsed from 800 AD onwards, it was partly because they were so densely populated and could not survive climate problems.
” ‘It’s suggesting that the landscape was just completely full of people at the onset of drought conditions and it didn’t have a lot of flexibility left. And so maybe the entire system basically unravelled as people moved farther away,’ says Mr Auld-Thomas.
“Warfare and the conquest of the region by Spanish invaders in the 16th century also contributed to eradication of Maya city states.
“Lidar technology has revolutionized how archaeologists survey areas covered in vegetation, like the Tropics, opening up a world of lost civilizations, explains Prof Canuto. …
” ‘I’ve got to go to Valeriana at some point. It’s so close to the road, how could you not? But I can’t say we will do a project there,’ says Mr Auld-Thomas. ‘One of the downsides of discovering lots of new Maya cities in the era of Lidar is that there are more of them than we can ever hope to study,’ he adds.
“The research is published in the academic journal Antiquity.“
More at the BBC, here. Seems to me the discovery was hardly an accident. Anyone with the patience to look at page 16 of a Google search deserves a bit more credit.


