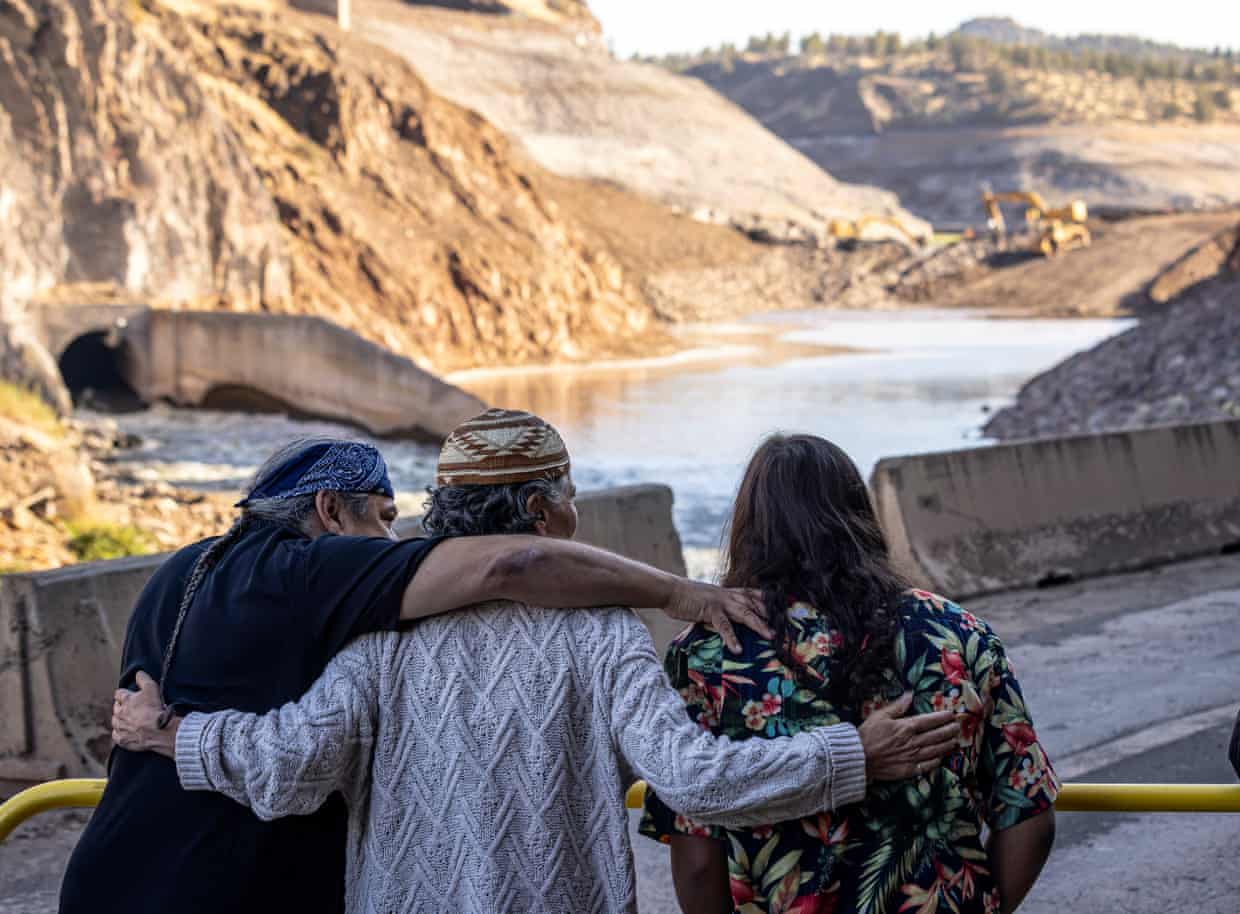
Photo: San Francisco Chronicle/Hearst Newspapers/Getty Images.
Leaf, Lisa and Chaas Hillman look on as construction crews allow the Klamath River to run freely for the first time in nearly a century, near Hornbrook, California, in August.
Everything done to Nature for human convenience has a downside. We have dammed up many rivers over the years for water reservoirs and electricity, flooding whole ecosystems. In the last couple of decades, though, we’ve been trying our best to restore what was lost, often with the guidance of indigenous tribes that always knew better.
Gabrielle Canon has one story at the Guardian.
“Explosions roared through the canyons lining the Klamath River [in 2024], signaling a new chapter for the region that hugs the Oregon-California border. In October, the removal of four hydroelectric dams built on the river was completed – the largest project of its kind in US history.
“The blast of the final dam was just the beginning. The work to restore the river, which winds 263 miles (423km) from the volcanic Cascade mountain range in Oregon to the Pacific coast in northern California, is now under way. …
” ‘It has been more successful than we ever imagined,’ said Ren Brownell, the spokesperson for the Klamath River Renewal Corporation, a nonprofit created to oversee and implement the removal. …
“The Klamath River was once an ecological powerhouse – the third-largest salmon-producing river in the American west. Its basin covered more than 9.4m acres (3.8m hectares) and its network of wetlands was the largest in the region. The ecosystem was home to millions of migrating birds. Tribes, including the Hoopa, Karuk, Klamath, Modoc and Yurok, thrived in this bountiful and beautiful watershed for thousands of years, with the river providing both sustenance and ritual.
“Over the last hundred years, these landscapes have been drastically altered.
“After the first dam began operating in 1918 – one of four that would eventually be forged in the lower Klamath to provide hydroelectric power to communities nearby – the course of the river was changed. The dams obstructed the migration of salmon and other native species, which help carry nutrients into the systems from the ocean, to cascading effects.
“They also held on to huge stores of sediment that would otherwise have flowed downriver, and created shallow reservoirs that quickly heated when the weather warmed. Increased water temperatures in the river allowed toxic algal blooms to thrive.
“In recent decades, the climate crisis has turned up the dial, deepening droughts and fueling a rise in catastrophic fire as the region grows ever hotter. The impacts only increased as more water was diverted to support the farming and ranching in the region, and more habitat was altered by mining and logging.
“Twenty-eight types of salmon and steelhead trout, seen as indicator species that represent the health of the ecosystems they live in, have been listed as threatened or endangered.
“As the Klamath ecosystem deteriorated, there was growing recognition that removing the dams would be a crucial first step in helping the region recover and build resilience in a warming world.
“But, faced with a strong resistance to change in local communities tucked around the reservoirs and a long history of difficult battles over water in the parched landscapes in the west, dam removal seemed all but impossible. The land for the dams was taken from tribes during the throes of colonization and development and more recently supported energy corporations that had shareholders to answer to.
“Then, in 2002, disaster struck. Algae flourished in the shallow warming waters that year, exacerbated by the dams and decisions from the US Bureau of Reclamation to divert vital flows to farms, leaving little for fish. The event killed 70,000 salmon and thousands of other species, resulting in one of the worst die-offs ever to occur in the US.
“The layers of fish floating belly-up sent an important signal of the horrors that could continue into the future if the dams remained. Forming a coalition, tribes up and down the Klamath launched a fierce campaign to educate the public, inform the shareholders of the companies that owned and operated the dams, and petition their boards. They protested and attended public hearings, and engaged with state and federal officials.
“It took decades of advocacy to convince PacifiCorp, a subsidiary of Berkshire Hathaway Energy, to let go of the aging infrastructure straddling the Oregon-California border. But in the mid-aughts, assured by shifts in public opinion and incentivized by the steep costs to relicense the dams, the company agreed it was time to see them go.
“In November 2020, nearly 20 years after the die-off, an agreement was forged between a long list of stakeholders that included tribal and state governments and federal agencies. The Klamath River Renewal Corporation was created to oversee and implement the removal.
“The organization had to help bring residents near the reservoirs onboard, navigate dozens of species-management plans, and model how outdoor-recreation enthusiasts could continue to enjoy the river. Ranchers and fishers, environmentalists and farmers, and locals and visitors all had connections to the basin, and were eager to weigh in. …
“Brownell, who grew up along the riverbanks, was standing in the canyon as the blast of the first dam released flows and the river that had been held over the last hundred years found its way back to itself. …
“There were moments of trauma along the way. Over the 100 years the dams were standing, they had held back 15m cubic yards of sediment. When the dams were removed, the heavy dead organic matter had to run downriver, soaking up oxygen in the water. Extensive modeling had predicted a severe impact on aquatic life, but no one knew how bad it would get or how long it would take for the river to regain its health. Some models predicted the suffocating conditions could linger for up to a month.
“ ‘I was braced and prepared but it was still tremendously hard,’ said Brownell, recalling how the water, rid of oxygen, looked like oil as it cascaded through its banks. ‘You can easily compare a river’s health to an individual’s health,’ she said. ‘Often when someone is sick, they are going to get worse before they get better. … The whole time everyone was so excited because it felt like the start of something – I just felt sick,’ she said.
“Leaf Hillman, a Karuk tribal ceremonial leader who has dedicated decades to seeing this project come to fruition, helped keep hopes high with assurances that these were signs of healing.
“ ‘For me it was beautiful,’ he said, recalling how he felt even when the rushing waters became clouded by silt. ‘I could envision what it was going to look like – a restored river.’
“In the end, the river lacked oxygen for only two 24-hour periods, a far shorter time than scientists had feared.”
At the Guardian, here, you can read what happened next. No paywall.