
Photo: Jeenah Moon/Bloomberg.
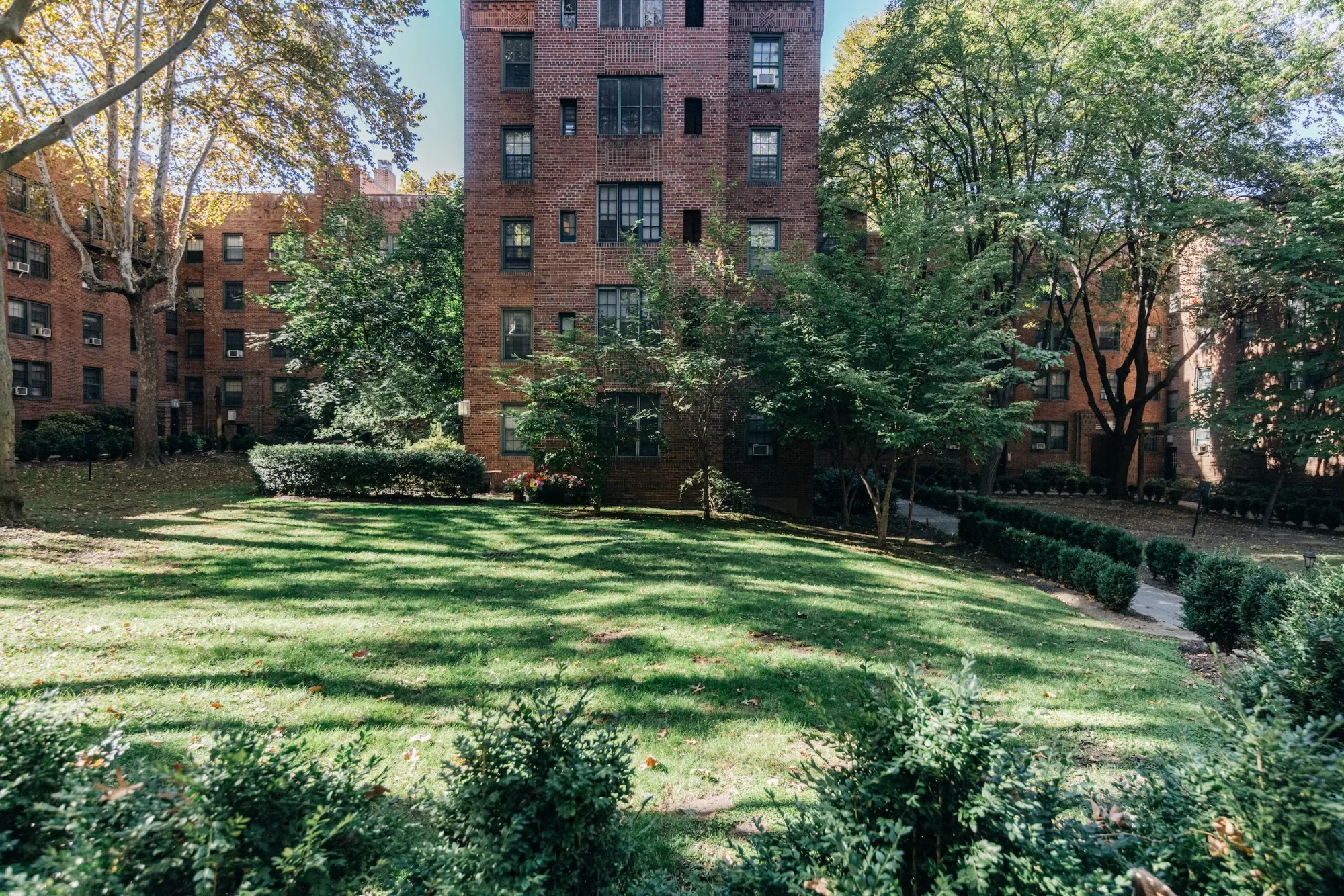
An interior courtyard at the Sunnyside Garden Apartments in Queens, New York. Completed in 1928, it remains a beacon of quality of life.
Growing up on the Copeland Estate in a suburb of New York, I would have been quite isolated from humanity if not for a scattering of nearby homes that had children. Having playmates meant so much to me. But for years, US community designers forgot about the importance of human interaction for both children and adults. One way to build it in, especially in cities, is the classic courtyard.
Alexandra Lange notes at Bloomberg CityLab that the shrinking population of children under five across the US “is bad news for the diversity and stability of cities, which are improved by the amenities that families seek — parks, public libraries, safe streets. It’s also discouraging for families who prefer to live in the city or don’t have the option or desire to move to the car-dominated suburbs. Any effort to retain families has to start with housing, their primary expense.
“That one weird trick for making cities more family-friendly? We’ve known it for decades: It’s the courtyard. …
“While Europe can claim centuries-old courts, America dabbled in them for decades, before the suburbs became the dominant housing type of both government subsidy and political propaganda.
“Courtyards don’t have to belong to the past. While textbook examples in brick and stone are lovely — and still home to thriving communities — contemporary architects are making courts in all sorts of materials, and for all types of housing, from apartments to townhomes.
“One of the first influential figures to advance the idea of the courtyard as the ideal urban type for families was Henry Darbishire, the mid-19th century English architect. His first patron, Angela Burdett-Coutts, was inspired by Charles Dickens and his novels of the urban poor to apply her wealth to reformist housing. ‘Nurturing the family and protecting children from the street was a huge part of the logic — turning the city inward,’ says Matthew G. Lasner, housing historian and the author of High Life: Condo Living in the Suburban Century.
“Architects and philanthropists quickly embraced an easily replicable courtyard model, with a single entrance on the street and interior vertical access off a planted court. The concept came to America in the 1870s via developers like Alfred Treadway White, responsible for the Cobble Hill Towers in Brooklyn. In the 1920s, more reformist developers — including everyone from the Rockefellers to communist unions — constructed many more of these courtyard projects.
“As architecture critic John Taylor Boyd wrote in 1920 of the Linden Court complex in Jackson Heights, the courtyard’s ‘benefits are apparent when it is remembered that the streets are the only playground of New York children, including the children of the rich.’ …
“When you’re talking courtyards in America, it’s hard to avoid Sunnyside Gardens. Not only does the Queens community remain one of New York City’s best neighborhoods, but it was home to one of America’s best critics, who made his affection clear.
“Lewis Mumford was one of the first residents of Sunnyside Gardens, completed in 1928, and constantly returned to its balance of private and public space, building and garden, in his analysis of other lesser New York City housing options. In “The Plight of the Prosperous,” published in the New Yorker in 1950, Mumford takes aim at the new white-brick residential buildings ‘that have sprung up since the war in the wealthy and fashionable parts of the city.’ While new low- and middle-income housing projects like his own ‘provide light and air and walks and sometimes even patches of grass and forsythia,’ these other private buildings, clustered in uptown rich neighborhoods, lack multiple exposures, outdoor space, cross-ventilation and quiet. …
“Clarence Stein and Henry Wright were the primary architects and planners behind Sunnyside Gardens, with Marjorie Sewell Cautley the landscape architect; all three would subsequently collaborate on Radburn, New Jersey, the ‘town for the motor age’ that in fact applied these communal principles for a result that we would now call transit-oriented development.
“The planners’ primary insight, in both the city and the suburbs, was to prioritize protected, communal open space over private yards or interior amenities. The courts, or courtyards, could be much larger if not subdivided by owner, and even in areas with public parks, having play space (and play companions) directly outside your door was a huge amenity. …
“On the West Coast, the courtyard evolved a little differently: surrounded by lower density, semi-detached houses with, eventually, a swimming pool in the center instead of a lawn. Irving Gill, considered the father of California modernism, designed prototype bungalow court in Santa Monica in the teens, with parking out of sight in the back and doorstep gardens. On tighter sites, U-shaped buildings with Spanish- and Italian-influenced architecture featured tiled fountains at center court. …
“ ‘When people have families with children, the home is important, but equally important are the people who are there with you,’ says Livable Cities president Meredith Wenskoski. “Your neighborhood is crucial. …
“Bay State Cohousing, a 30-unit development outside Boston, has common amenities as part of its charter, including a shared kitchen and activity rooms. But the pastel, clapboard complex, intended to blend in with single-family neighbors, also forms a U around a southwest-facing courtyard, with outdoor circulation providing plenty of opportunities for casual run-ins with the neighbors.
“ ‘The courtyard is a nested boundary that allows interaction with other children, and more importantly, with other adults who become a kind of network,’ says Jenny French, whose firm French 2D designed Bay State. ‘In an urban setting, the barrier that the contemporary parent has to letting their child out the door, thinking about the car-dominated city where they are unable to play in the street – the courtyard is a natural alternative.’
“French, who has also been coordinating the housing studio at the Harvard Graduate School of Design for seven years, can’t help but extend these design observations into the cultural and political spheres. Everyone talks about loneliness in America for people of all ages. For teens and seniors alike, French sees a solution. It’s one we’ve had all along: ‘Could a courtyard house actually be the friendship apparatus we need?’ ”
Lots more at Bloomberg, here.



 Photo: Rafael Herrin-Ferri/Architectural League of New York
Photo: Rafael Herrin-Ferri/Architectural League of New York


